

In this paper, we bring forth the current advances made in CAR-T cell therapy for AML treatment as found in published data in the form of case reports, case series, and clinical trials. The road to successful introduction and incorporation of CAR-T cell therapy to the treatment of AML has some key roadblocks that include, but are not limited to, antigenic heterogeneity that is prevalent in AML the AML tumor microenvironment and on-target off-tumor toxicities ( 12). The use of CAR-T cell therapy is now being investigated for the treatment of AML ( 11). The treatment options for the relapsed disease are limited and median overall survival is in months after the disease relapse ( 6).Ĭhimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has shown promising results for the treatment of chemotherapy-refractory B cell malignancies, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and B cell lymphoma as well as for multiple myeloma ( 7– 10). However, 50% of patients that undergo HSCT and 80% of the patients that are not eligible or while waiting for HSCT will eventually relapse and die of the disease ( 5).
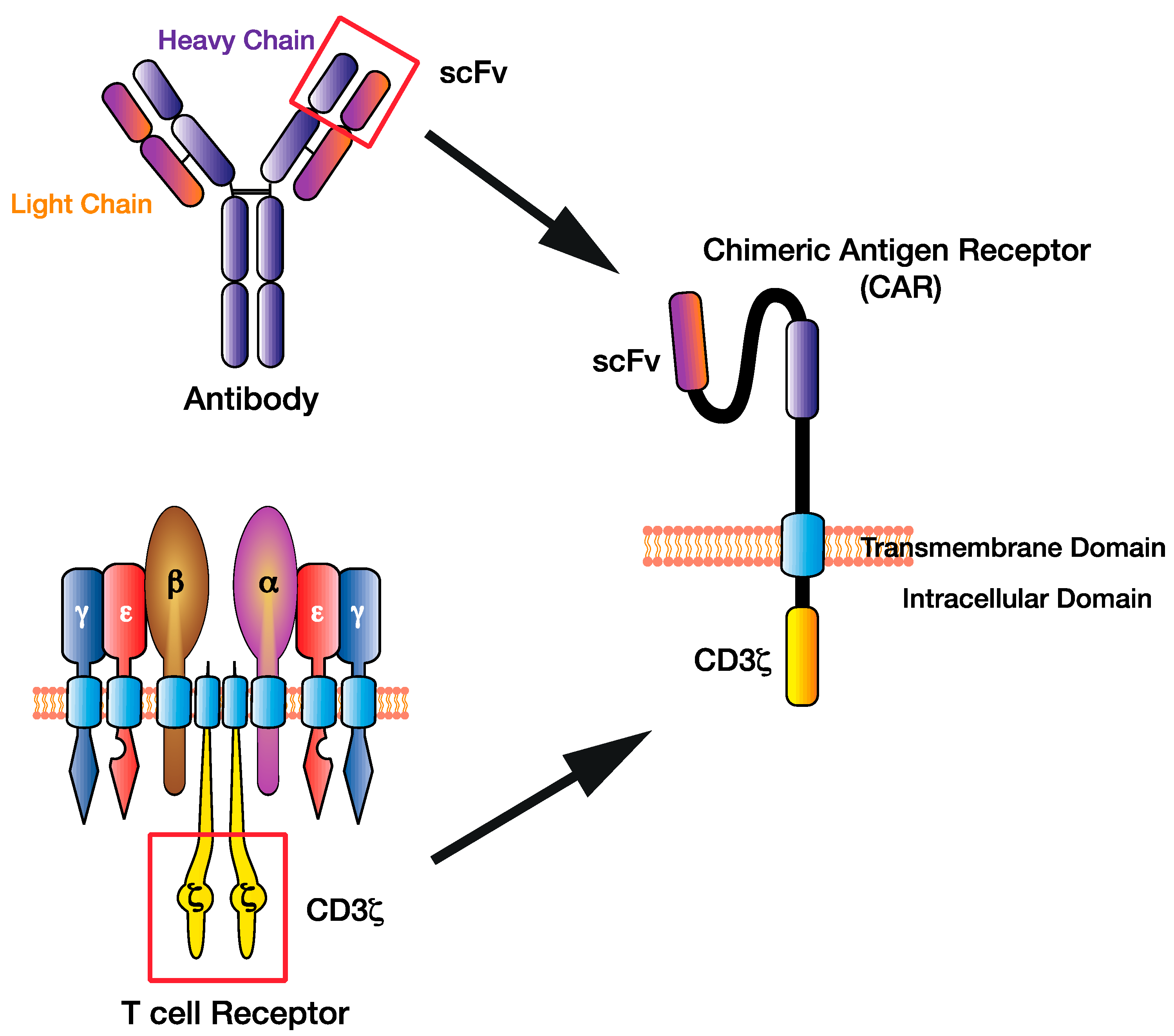
Allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) is deemed as the only definitive treatment for AML at this time for intermediate and high-risk patients, as it is expected to result in long-lasting complete remission (CR) ( 4). At the time of diagnosis, in most cases the disease initially responds to high-dose induction chemotherapy ( 3) nevertheless, 10-40% of patients are primarily refractory to induction chemotherapy ( 2). The prognosis of AML is poor, with a cure rate of a mere 5-15% in patients above age 60 years, and 35-40% in patients younger than 60 years ( 2). Major challenges include heterogeneous disease biology, lack of a unique targetable antigen, and immune exhaustion.Īcute myeloid leukemia (AML) accounts for only 1% of all new cancers in the United States and remains one of the most aggressive hematological malignancies in adults with a 5-year survival rate of 30.5% ( 1). The pooled incidence of cytokine release syndrome, immune-effector cell associated neurotoxicity syndrome, and graft-versus-host disease was estimated as 54.4% (95% CI 0.17-0.90, I 2 =77%), 3.9% (95% CI 0.00-0.19, I 2 =22%), and 1.6% (95%CI 0.00-0.21, I 2 =33%), respectively.Ĭonclusion: CAR-T therapy has demonstrated modest efficacy in RR-AML. Results: We analyzed 57 patients from 10 clinical trials and 3 case reports. Proportions with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were computed. Pooled analysis was done using the meta-package by Schwarzer et al. Data was extracted following PRISMA guidelines. After screening 677 manuscripts, 13 studies were included. Methods: We performed a literature search on PubMed, Cochrane Library, and. 4Division of Hematology/Oncology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health, Madison, WL, United Statesīackground: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate outcomes following chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (RR-AML).3Division of Hematology/Oncology, Roswell Park Cancer Institute Buffalo, NY, United States.2Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, United States.1Division of Hematologic Malignancies & Cellular Therapeutics, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, KS, United States.Moazzam Shahzad 1,2, Andrea Nguyen 1, Ali Hussain 1, Mohammad Ammad-Ud-Din 2, Muhammad Salman Faisal 3, Ezza Tariq 1, Fatima Ali 1, Atif Butt 1, Iqra Anwar 1, Sibgha Gull Chaudhary 1, Forat Lutfi 1, Nausheen Ahmed 1, Anurag K.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
